Trapped in Debt: How China's lending practices are hurting developing countries
China's lending practices have come under scrutiny in recent years, as developing countries around the world find themselves increasingly indebted to the Asian giant. While China's loans have been celebrated for helping to finance infrastructure projects in countries that struggle to secure funding from traditional sources, the reality is that these loans are often trapping these nations in a cycle of debt that is difficult to break free from.
 |
| Chinese debt trap diplomacy credits The Indian Express |
One of the main concerns with China's lending practices is the lack of transparency. Unlike loans from traditional lenders such as the World Bank and IMF, China's loans are often made through state-owned banks and other government-controlled entities. This means that the terms and conditions of these loans are not always made public, making it difficult for countries to fully understand the implications of taking on this debt. Additionally, many of these loans are tied to specific infrastructure projects, which can limit a country's ability to use the funds for other purposes.
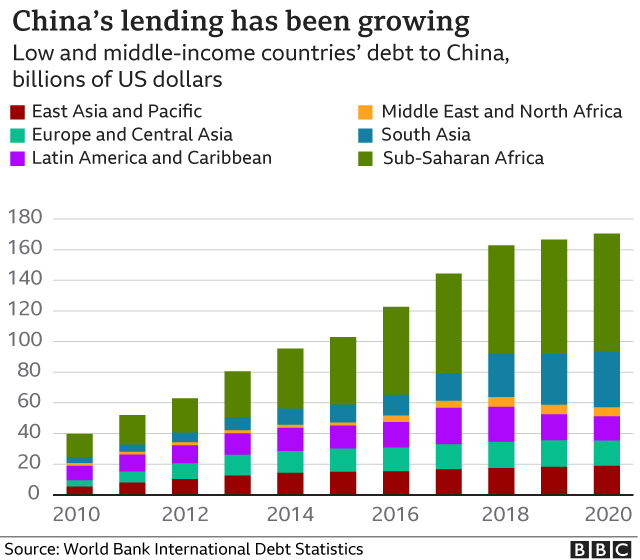 |
| credits BBC |
Another issue with China's lending practices is the high-interest rates that many countries are paying on these loans. In some cases, the interest rates on Chinese loans are significantly higher than those offered by other lenders, making it even more difficult for these countries to repay the debt. Additionally, many of these loans are denominated in Chinese currency, which can create additional risks for countries if the value of their own currency falls relative to the Chinese yuan.
The problem is especially severe for countries that are already in a debt crisis. Sri Lanka, for example, was forced to hand over control of its Hambantota port to China on a 99-year lease after it failed to repay Chinese loans. Similarly, Pakistan has been struggling to repay Chinese loans for the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, which has led to concerns about the country's ability to maintain control over its own infrastructure.
 |
| Hambantota Port in south cost, Sri Lanka credits Maritime Gateway |
One of the most significant issues with China's lending practices is the potential for these loans to become a political tool. Because many of these loans are tied to specific infrastructure projects, countries that take on this debt can be pressured to make political concessions to China. This is particularly concerning in countries that have weak governance structures, as these loans can be used to gain political influence and control.
 |
| Massive infrastructure project by China credits Asia times |
In conclusion, while China's lending practices have helped to finance infrastructure projects in developing countries, the reality is that these loans are often trapping these nations in a cycle of debt that is difficult to break free from. The lack of transparency, high-interest rates, and political implications of these loans are all cause for concern. It is important that developing countries are aware of the risks associated with taking on debt from China and consider alternative sources of funding to avoid becoming trapped in debt.
Comments
Post a Comment